GitHub Actions
以下示例展示了如何将 Turborepo 与 GitHub Actions 结合使用。
¥The following example shows how to use Turborepo with GitHub Actions.
对于给定的根 package.json:
¥For a given root package.json:
以及 turbo.json:
¥And a turbo.json:


在你的代码库中创建一个名为 .github/workflows/ci.yml 的文件,其中包含以下内容:
¥Create a file called .github/workflows/ci.yml in your repository with the following contents:
使用 Vercel 远程缓存进行远程缓存
¥Remote Caching with Vercel Remote Cache
要将远程缓存与 GitHub Actions 结合使用,请将以下环境变量添加到你的 GitHub Actions 工作流程中,以使其可用于你的 turbo 命令。
¥To use Remote Caching with GitHub Actions, add the following environment variables to your GitHub Actions workflow
to make them available to your turbo commands.
-
TURBO_TOKEN- 用于访问远程缓存的 Bearer 令牌¥
TURBO_TOKEN- The Bearer token to access the Remote Cache -
TURBO_TEAM- Vercel 团队用于共享工件的 slug¥
TURBO_TEAM- The slug of the Vercel team to share the artifacts with
要使用远程缓存,请检索提供程序的远程缓存的团队和令牌。在此示例中,我们将使用 Vercel 远程缓存。
¥To use Remote Caching, retrieve the team and token for the Remote Cache for your provider. In this example, we'll use Vercel Remote Cache.
在 Vercel 仪表板 中为你的账户创建一个作用域访问令牌
¥Create a Scoped Access Token to your account in the Vercel Dashboard
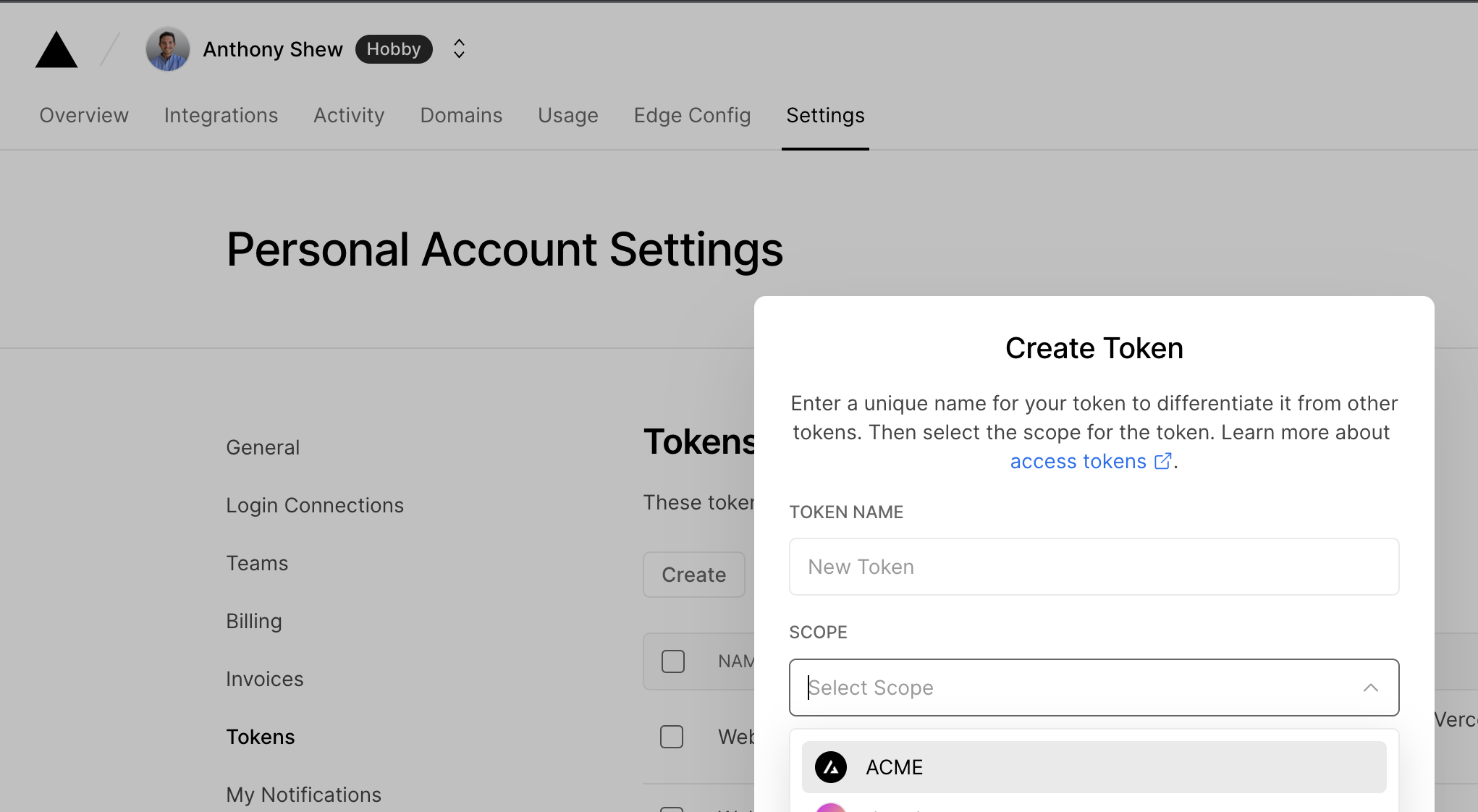
将值复制到安全的地方。你稍后会需要它。
¥Copy the value to a safe place. You'll need it in a moment.
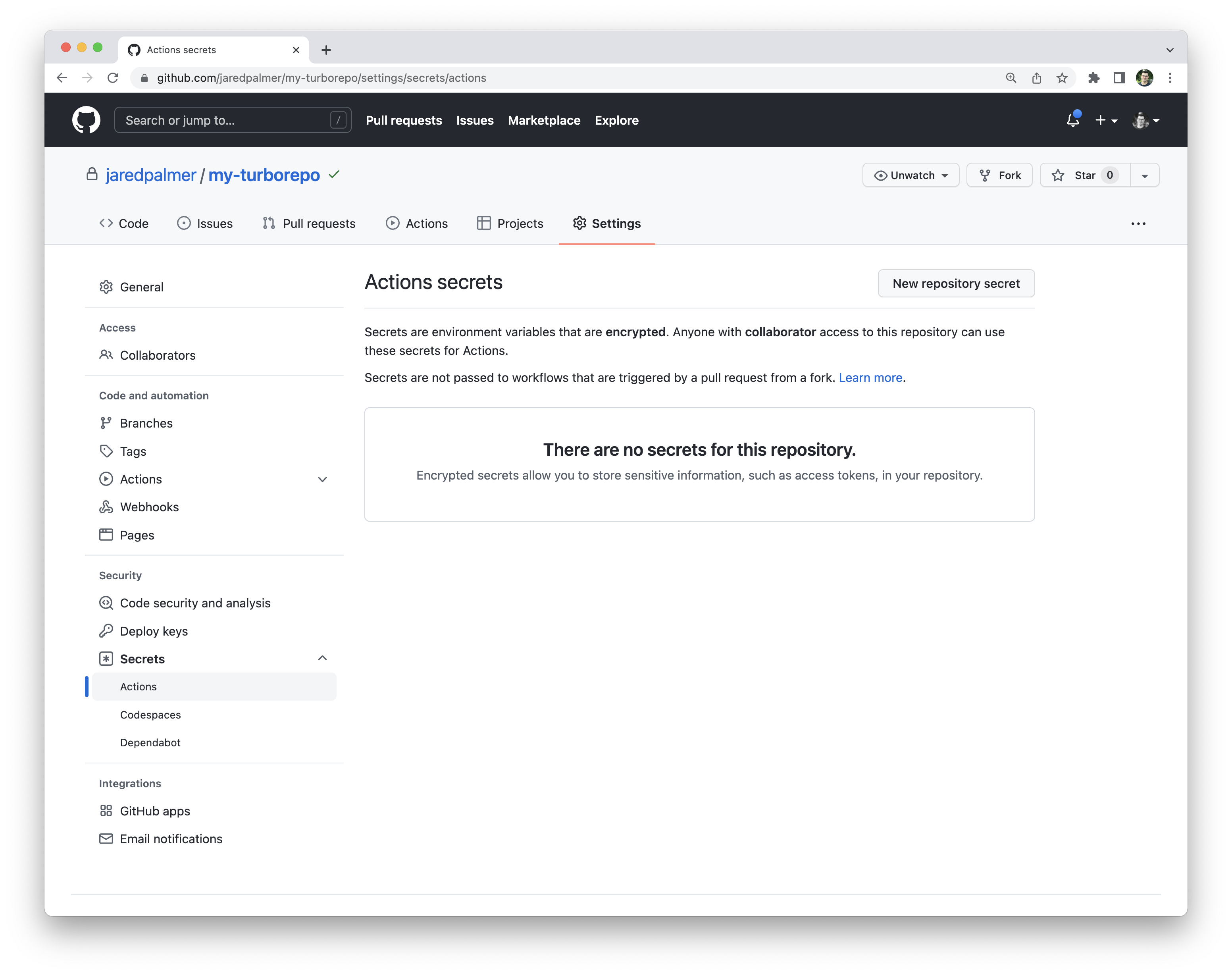
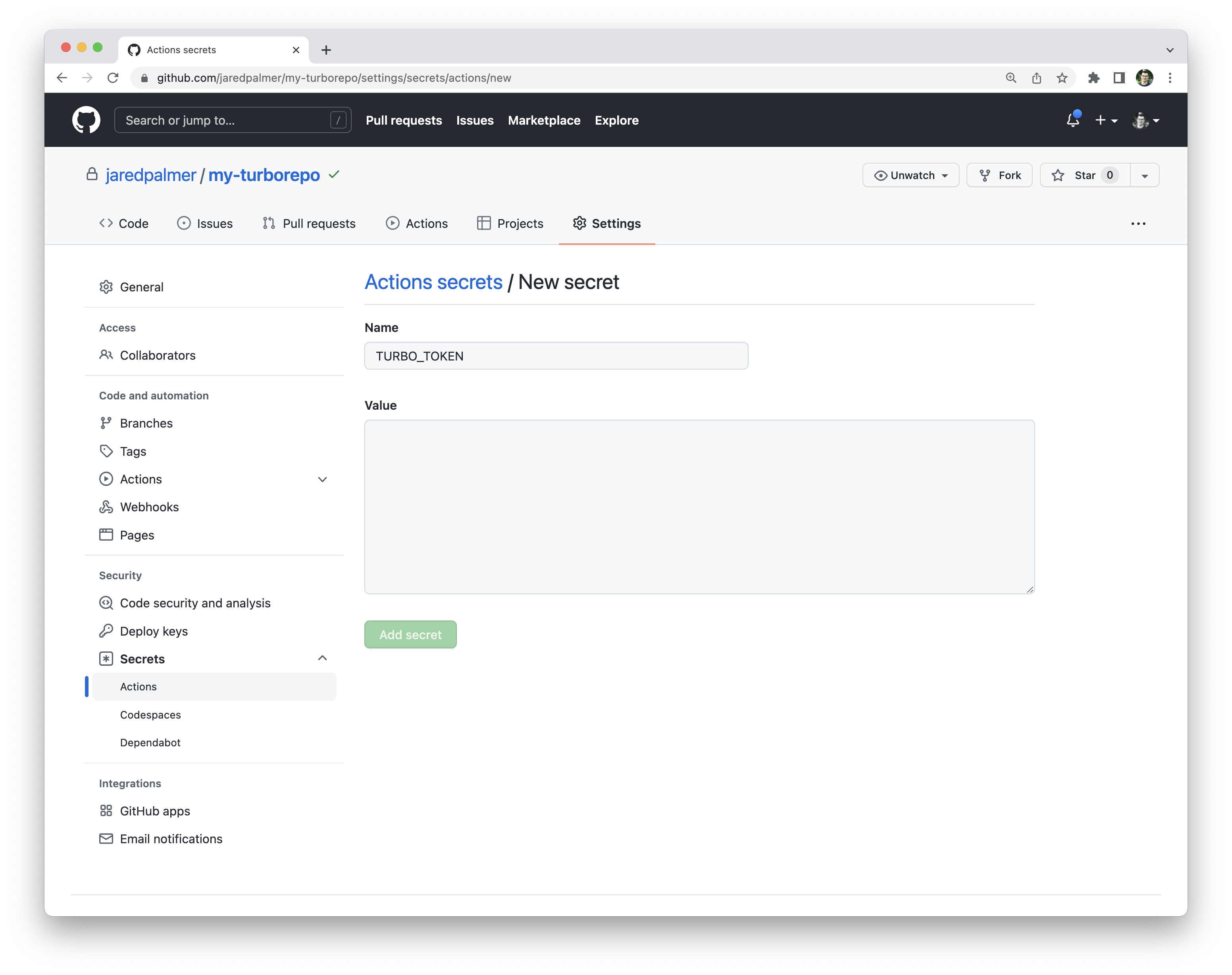
转到 GitHub 仓库设置,然后点击“Secrets”选项卡,然后点击“Actions”选项卡。创建一个名为 TURBO_TOKEN 的新密钥,并输入你的作用域访问令牌的值。
¥Go to your GitHub repository settings and click on the Secrets and then Actions tab. Create a new secret called TURBO_TOKEN and enter the value of your Scoped Access Token.
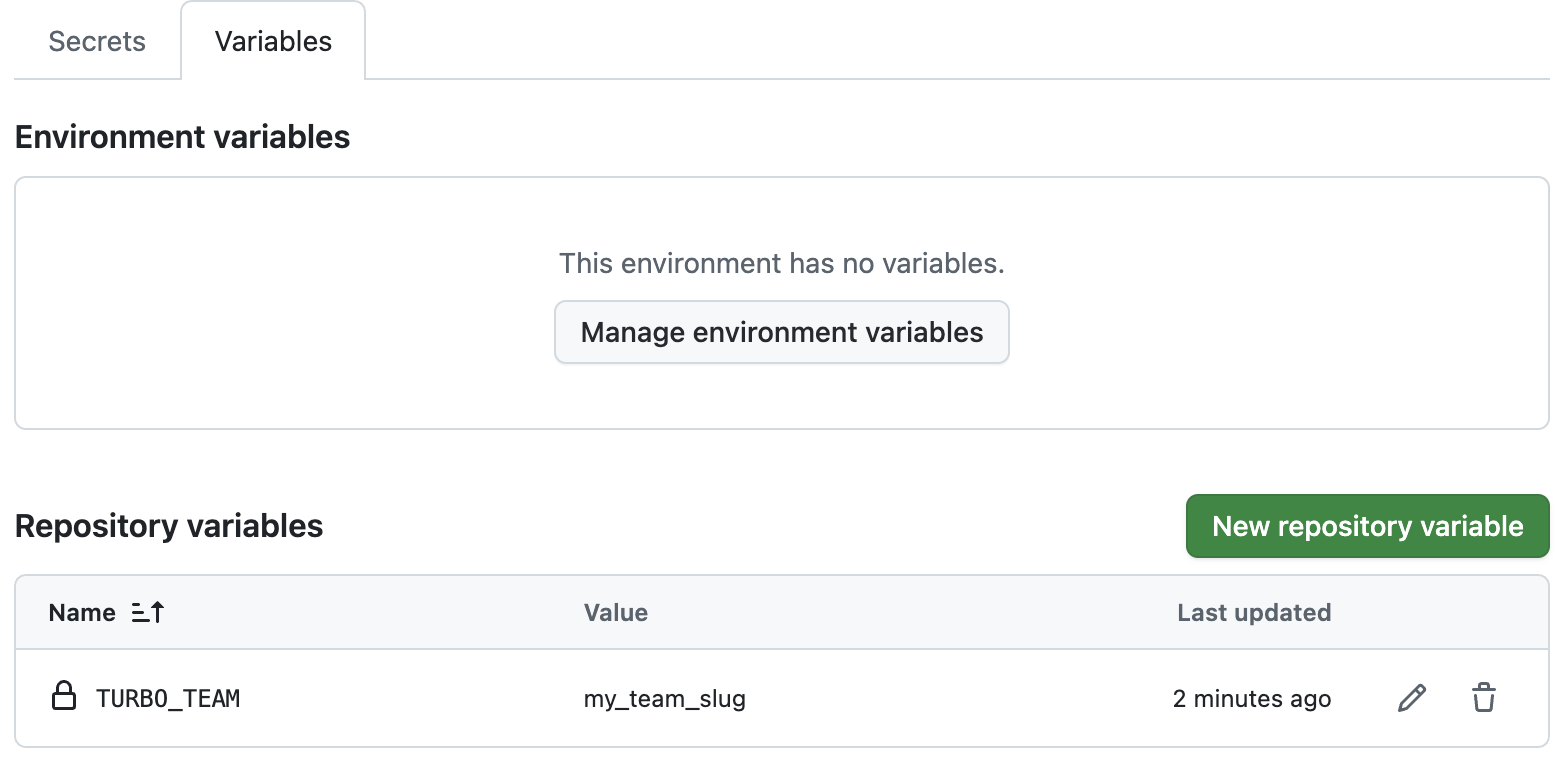
创建一个名为 TURBO_TEAM 的新存储库变量(单击“变量”选项卡),并将其设置为你的团队别名。 - 你的团队 URL 中 vercel.com/ 之后的部分。例如,vercel.com/acme 的别名是 acme。
¥Create a new repository variable (click the Variables tab) called TURBO_TEAM and set it to your team slug - the part after vercel.com/ in your Team URL. For example, the slug for vercel.com/acme is acme.
Good to know:
使用仓库变量而不是 secret 将阻止 GitHub Actions 在日志输出中屏蔽你的团队名称。
¥Using a repository variable rather than a secret will keep GitHub Actions from censoring your team name in log output.
在 GitHub Actions 工作流程的顶部,为使用 turbo 的作业提供以下环境变量:
¥At the top of your GitHub Actions workflow, provide the following environment variables to jobs that use turbo:
使用远程缓存和可重用工作流
¥Using Remote Caching with Reusable Workflows
有关将密钥传递给可重用工作流的信息,请参阅 GitHub 文档:如何将密钥传递给嵌套工作流。
¥For information on passing secrets to reusable workflows, see GitHub's documentation on passing secrets to nested workflows.
使用 GitHub actions/cache 进行远程缓存
¥Remote Caching with GitHub actions/cache
以下步骤展示了如何使用 actions/cache 在 GitHub 上缓存你的 monorepo 工件。
¥The following steps show how you could use actions/cache to cache your monorepo artifacts on GitHub.
提供一个 package.json 脚本,该脚本将使用 Turborepo 运行任务。
¥Supply a package.json script that will run tasks using Turborepo.
示例 package.json 和 build 脚本:
¥Example package.json with a build script:
在 CI 文件的构建步骤之前,配置 GitHub 流水线,并使用 actions/cache@v4 操作。
¥Configure your GitHub pipeline with a step which uses the actions/cache@v4 action before the build steps of your CI file.
-
确保
actions/cache操作中设置的path属性与上面的输出位置匹配。在下面的示例中,path设置为.turbo。¥Make sure that the
pathattribute set within theactions/cacheaction matches the output location above. In the example below,pathwas set to.turbo. -
在
key属性下声明当前运行的缓存键。在下面的示例中,我们使用运行器操作系统和 GitHub SHA 的组合作为缓存键。¥State the cache key for the current run under the
keyattribute. In the example below, we used a combination of the runner os and GitHub sha as the cache key. -
在
restore-keys属性下声明所需的缓存前缀模式。确保此模式在未来的 CI 运行中仍然有效。在下面的示例中,我们使用${{ runner.os }}-turbo-作为缓存键前缀模式进行搜索。这允许我们在任何后续 CI 运行中访问缓存,即使github.sha发生变化。¥State the desired cache prefix pattern under the
restore-keysattribute. Make sure this pattern will remain valid for future ci runs. In the example below, we used the${{ runner.os }}-turbo-as the cache key prefix pattern to search against. This allows us to hit the cache on any subsequent ci runs despitegithub.shachanging.
示例 ci yaml 文件,其中 .turbo 为选定的缓存文件夹:
¥Example ci yaml with .turbo as chosen cache folder: